International trade involves exchanging goods and services across borders, requiring various payment methods to ensure smooth transactions.
Generally, payment methods in international trade depend on the trust level between importers and exporters, the risks involved, and market norms based on product types.
Here are the four most commonly used methods:
1. Letter of Credit (L/C)
What is a letter of credit in global trade?
A letter of credit, or documentary credit, is a contractual agreement where the issuing bank (importer’s bank) guarantees payment to the exporter on behalf of the importer.
This payment is made against the receipt of specified, compliant documents. The issuing bank often collaborates with intermediary banks to complete the transaction and ensure payment to the exporter.
While a letter of credit is highly reliable for buyers and sellers, it isn’t suitable for businesses lacking credibility or low-value transactions due to the associated costs.
You should also note that this payment method carries risks. Specifically, sellers are only paid once they meet all the specified requirements in the letter, which can be more detailed.
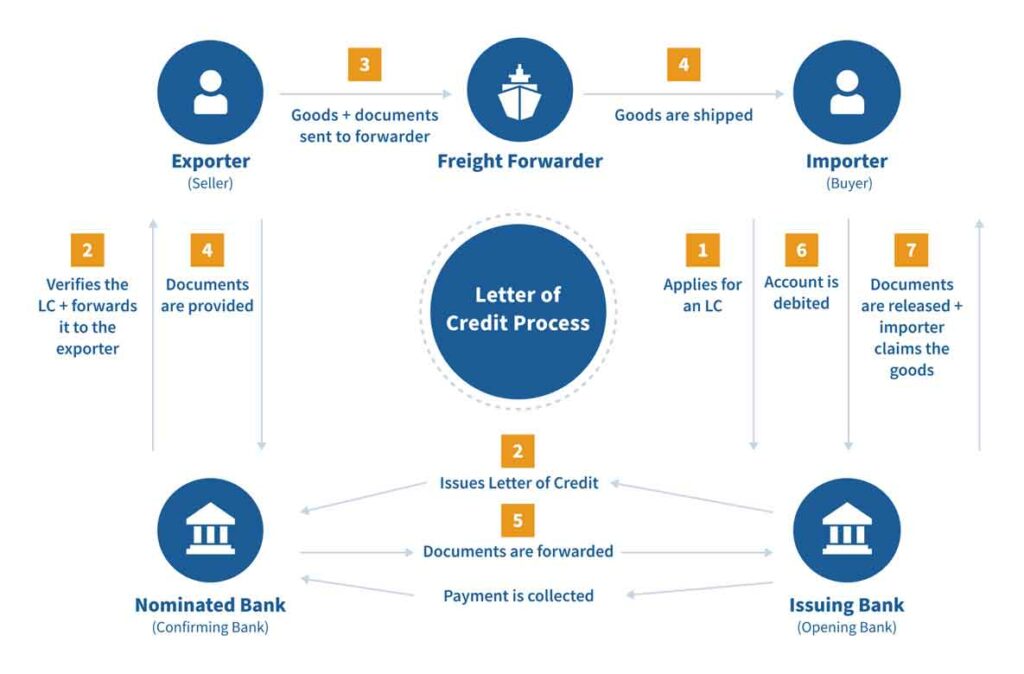
The advantages of a letter of credit
LCs are particularly valuable when reliable credit information about a foreign buyer is difficult to obtain or when the buyer’s credit is questionable.
As LCs are credit instruments, they leverage the importer’s credit with their bank to secure the LC, with the importer paying a fee for this service.
This payment method also safeguards the importer, as the required documents can confirm that the goods have been shipped as per agreement.
Therefore, Letters of Credit are among the most flexible and secure tools available for international trade.
2. Cash In Advance (CIA)
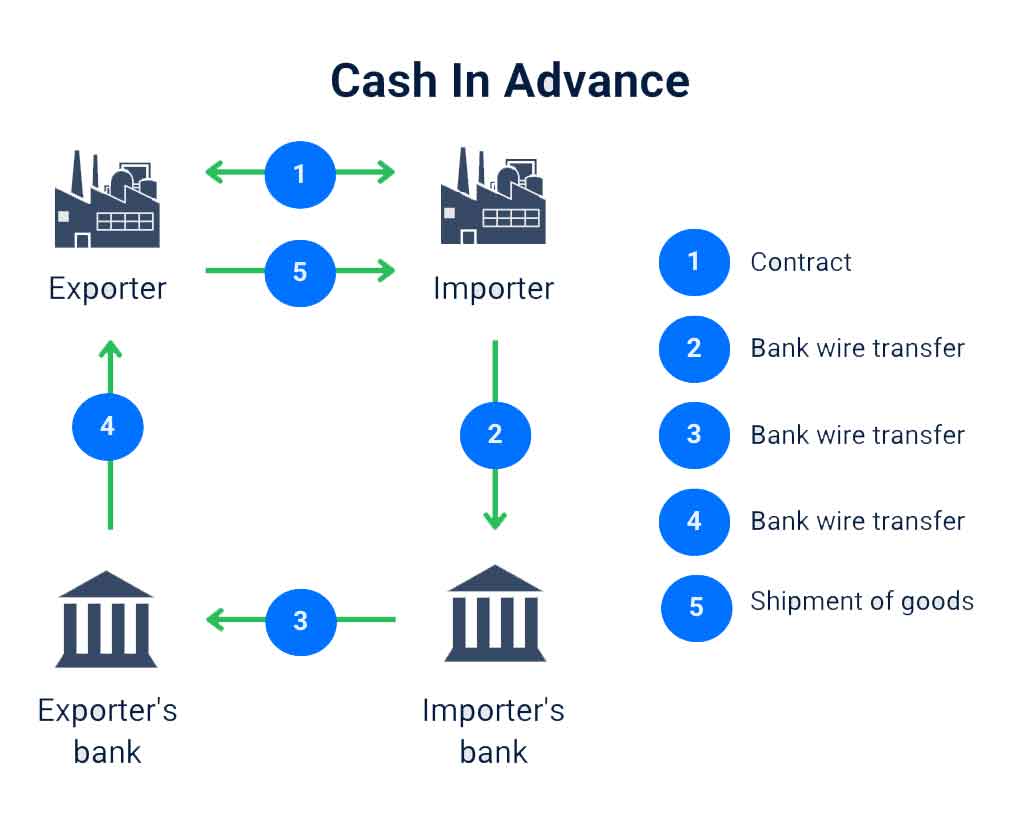
Cash In Advance, also known as advance payment or pre-payment, is one of the safest payment methods for sellers.
In this arrangement, the buyer pays the full invoice amount to the seller before the goods are shipped.
This approach places all the risk on the buyer, as they pay for goods they have not yet received. However, from the seller’s perspective, it is ideal because it guarantees payment before shipping the goods.
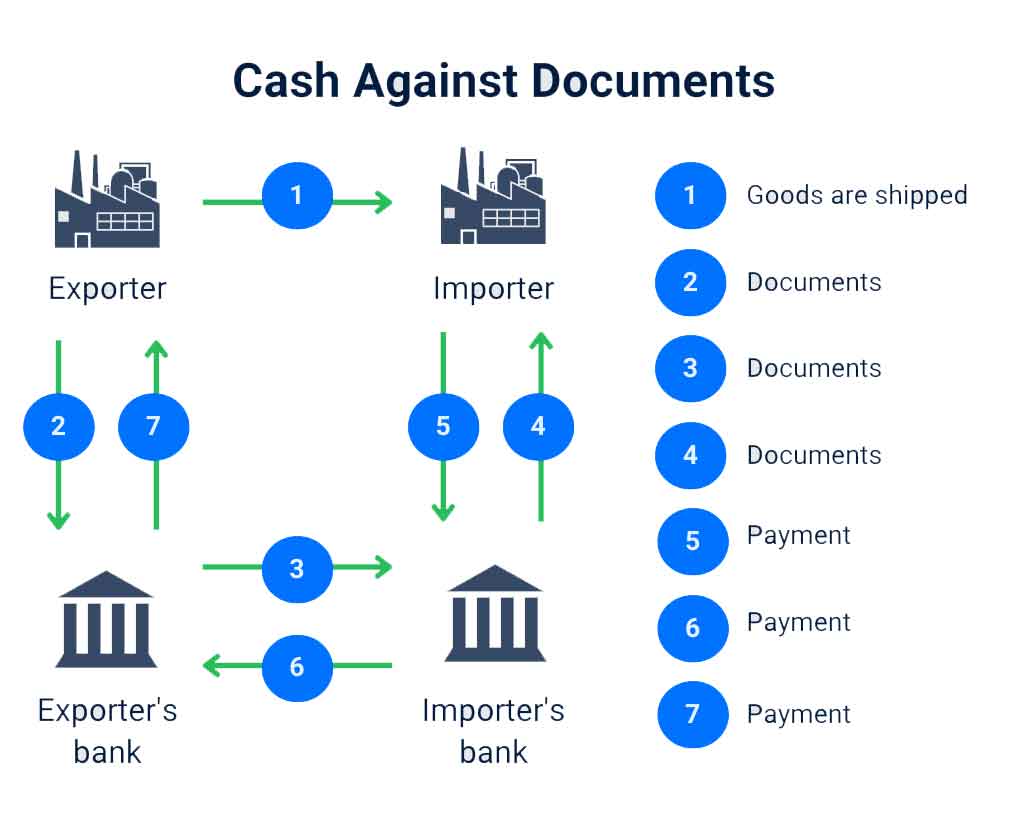
3. Cash Against Documents (CAD)
With this payment method, the buyer pays the seller after receiving documents that confirm ownership of the goods, such as a bill of lading or a bill of exchange.
Funds are essentially held in escrow until these documents are received. This method is often used when the buyer and seller are not well acquainted or when the buyer wants to mitigate the risk of non-delivery.
4. Acceptance Credit
It involves an importer obtaining a loan from a bank to pay for purchased goods. The importer then repays this loan, with interest, over a set period.
Acceptance credit is favored because it allows importers to finance the purchases and manage repayment costs.
There are three primary means of acceptance credit:
Letter of Credit with Acceptance Credit
It allows the release of shipping documents for payment upon policy maturity. Payment is made after the importer’s or correspondent bank accepts the policy presented with these documents.
Against Documents with Acceptance Credit
Under this method, the importer settles the payment upon the policy’s maturity after the bank provides the shipping documents along with the attached policy.
Against Goods with Acceptance Credit
Here, the importer makes payment once they have received the goods and accepted the policy, settling the amount at the policy’s maturity.
How do you choose the right payment method?
In international trade, selecting the appropriate payment method is crucial to safeguarding both involved parties.
Consider the following factors when deciding:
- The value of the traded goods
- The nature of the exchanged goods
- The risk tolerance of each party
- The cost and duration of shipping
Which payment method is best?
There is no one-size-fits-all “best” payment method for international trade. The ideal choice aligns with the requirements of both the buyer and the seller while minimizing potential risks.
Conclusion
In the fiercely competitive shipping industry, gaining any advantage can make a significant difference. Selecting a suitable payment method is a prime way to stay ahead.
For sellers, offering the payment method preferred by buyers can enhance your chances of securing a sale.
For buyers, choosing a payment method that reduces risks and boosts negotiating leverage can help you secure the best terms from the seller.
At ASLG international transport, we offer a range of flexible payment options tailored to meet your needs. Contact us today for a quote and discover how our diverse payment methods can benefit your business!




