Most lithium batteries must comply with Section 38.3 of the UN Manual of Tests and Criteria, known as the UN 38.3 test. It ensures they meet safety standards for transport, as these power sources can be flammable and explosive. In this post, we’ll explore the UN 38.3 standards and requirements, as well as how they guarantee the safe transport of batteries.
Table of Contents:
What is UN 38.3 testing?
UN 38.3 refers to international standards for transporting lithium-ion batteries by air, land, and sea. These regulations aim to monitor the batteries that meet safety requirements during shipping to minimize risks.
The UN 38.3 transportation test covers several key aspects, including:
Packaging guidelines
Packaging must include insulation materials to prevent direct contact between battery terminals and other conductive surfaces. Additionally, batteries should be secured, preventing movement, punctures, or short-circuiting during transit.
Labeling requirements
Every lithium-ion battery shipment must be accurately labeled with the required shipping information, such as the shipper’s and consignee’s names and addresses, along with a clear description of the contents. These labeling standards are in place to ensure that shipments are properly documented and handled during transportation.
Testing procedures
Before transport, batteries must undergo various tests designed to prove their safety. This step is critical in ensuring compliance with the UN DOT 38.3 lithium battery transportation standards.
Safety measures
Shipping lithium batteries internationally must include a safety data sheet that provides detailed information on any hazards associated with the shipment.
Example of UN38.3 test report
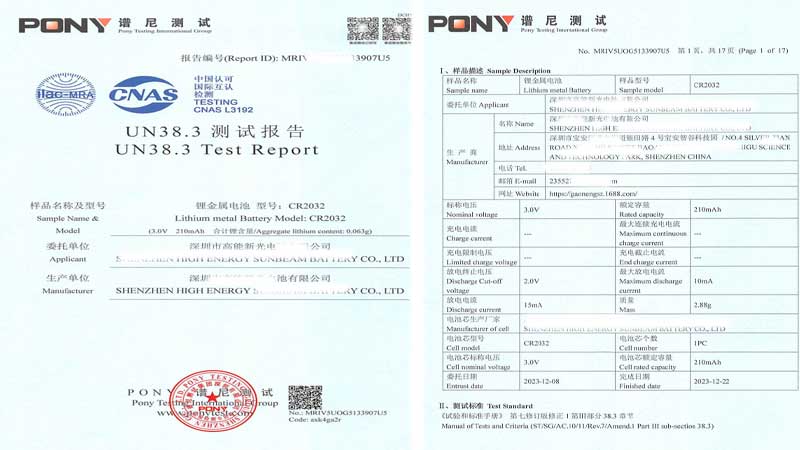
Is UN 38.3 mandatory?
Yes, UN 38.3 compliance is mandatory for nearly all lithium batteries.
What types of batteries does UN 38.3 cover?
- Lithium-ion battery packs: These are groups of one or more cells connected to provide power to devices. Battery packs must meet specific UN DOT 38.3 standards.
- Lithium-ion cells:A cell is the basic unit of a battery, comprising a positive electrode, a negative electrode, and an electrolyte.
- Spent (Discharged) lithium-ion cells and battery packs:Even used or fully discharged lithium cells and battery packs should be transported under the UN 38.3 test to ensure they aren’t accidentally recharged, which could pose a fire hazard.
Why are lithium batteries subject to testing?
Nowadays, lithium-ion batteries power most modern devices, from smartphones and laptops to power tools, electric vehicles, and even electricity grids. However, poorly designed lithium batteries can present serious risks like fires or explosions.
By conducting the required UN 38.3 tests, you can:
- Lower insurance premiums
- Ensure the safe and legal transport of your battery products.
- Save time and costs with reliable, standardized testing procedures.
- Gain a competitive edge by entering new markets more efficiently.
- Improved safety for employees handling and shipping batteries
- Strengthened reputation for delivering high-quality, safe products
What types of tests are conducted under UN 38.3?
Altitude Test:
This test simulates high-altitude environments to ensure the battery stays safe during air freight. The test places the battery in a chamber and exposes it to altitudes of up to 15,000 feet (4,572 meters).
Vibration Test:
To assess the battery’s durability under vibration, it sits on a vibrating platform and experiences frequencies ranging from 5 to 200 Hz. It simulates the vibrations encountered during road, sea, or air transport.
Shock Test:
This test checks the battery’s resilience against sudden shocks. The battery undergoes impacts of up to 150 Gs to ensure it can withstand the harsh conditions of transport.
Thermal Test:
This test ensures the battery can handle extreme temperature fluctuations. It goes through a temperature range of -40°C (-40°F) to 85°C (185°F), mimicking the conditions it may face in various climates during shipping.
External Short Circuit:
Tests the battery’s ability to prevent fires or explosions when exposed to external conductive materials.
Impact/Crush Test:
Simulates crushing forces to ensure the battery doesn’t rupture or ignite under pressure.
Overcharge Test:
Verifies that safety systems prevent overheating or thermal runaway during overcharging.
Forced Discharge Test:
Ensures the battery remains safe and doesn’t fail dangerously under abnormal discharge conditions.
What is the difference between MSDS and UN 38.3?
The Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) offers comprehensive information about the properties and hazards of specific chemicals, including guidelines for safe handling, storage, and emergency procedures. This document applies to most hazardous materials, not just lithium batteries.
In contrast, the UN 38.3 test report addresses the safe transportation of lithium batteries. It outlines the testing standards that these batteries must meet to ensure safe transport without posing risks.
It’s necessary to conduct UN 38.3 testing through a certified third-party testing organization. Conversely, the MSDS can be prepared by the manufacturer or provided to a third-party testing company.
How long is a UN 38.3 test report valid for?
Typically, the UN 38.3 certification remains valid for one year. Shippers should regularly evaluate their batteries and retest them as necessary, especially if they implement any design changes or introduce new materials. Additionally, it’s wise to stay updated on any changes in regulations or testing criteria that could impact the validity of the UN 38.3 test report.
How to obtain UN 38.3 certification?
Choose a reputable third-party testing organization specializing in UN 38.3 assessments, such as Intertek. These companies have the essential expertise and equipment to determine whether your batteries meet the stringent safety standards for transportation.
After getting a testing report, you can send your batteries to our experts, who will customize the best logistics solution to suit your needs.
Additionally, our team offers ongoing support and guidance regarding regulatory changes, assisting you in navigating the complexities of lithium battery transportation and compliance.




